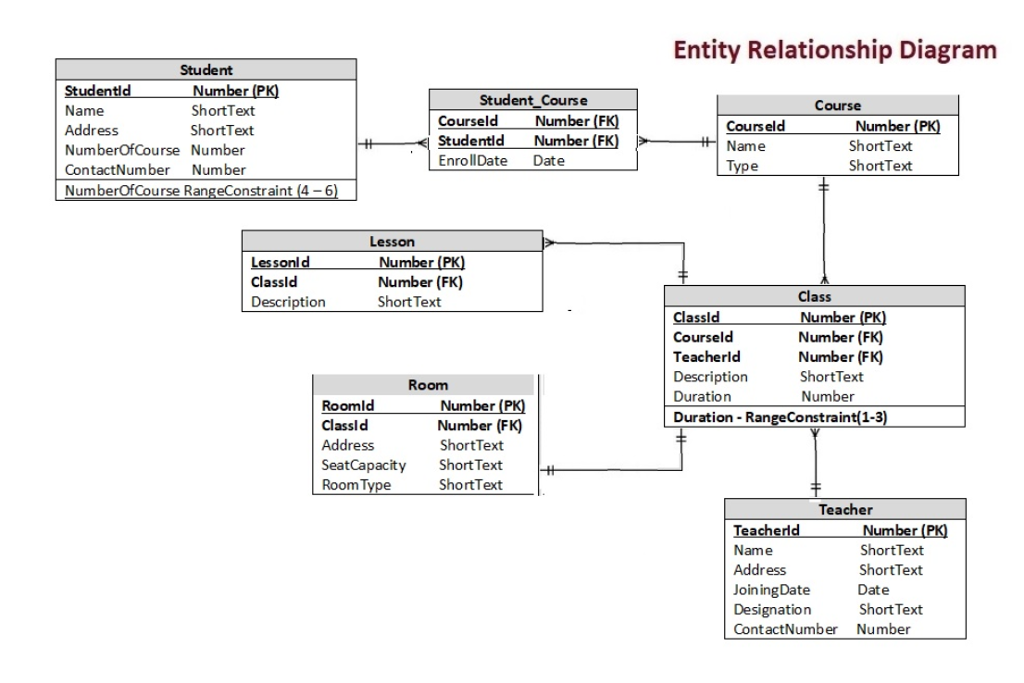
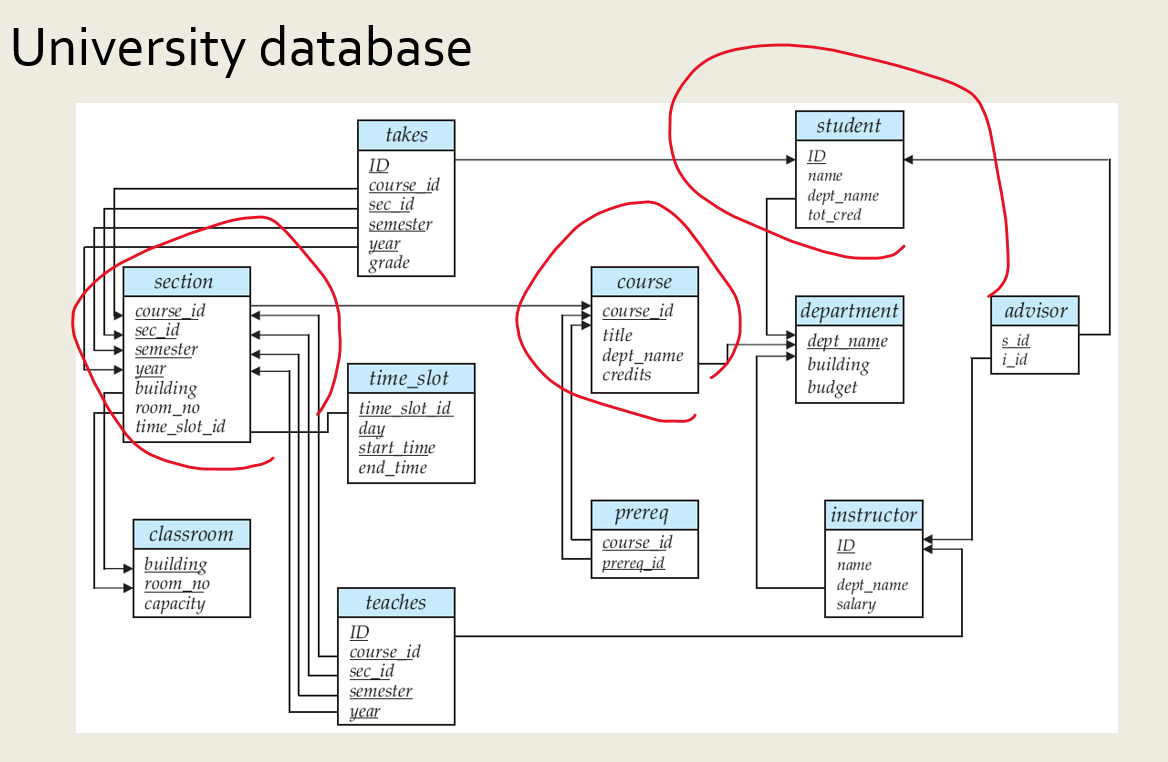
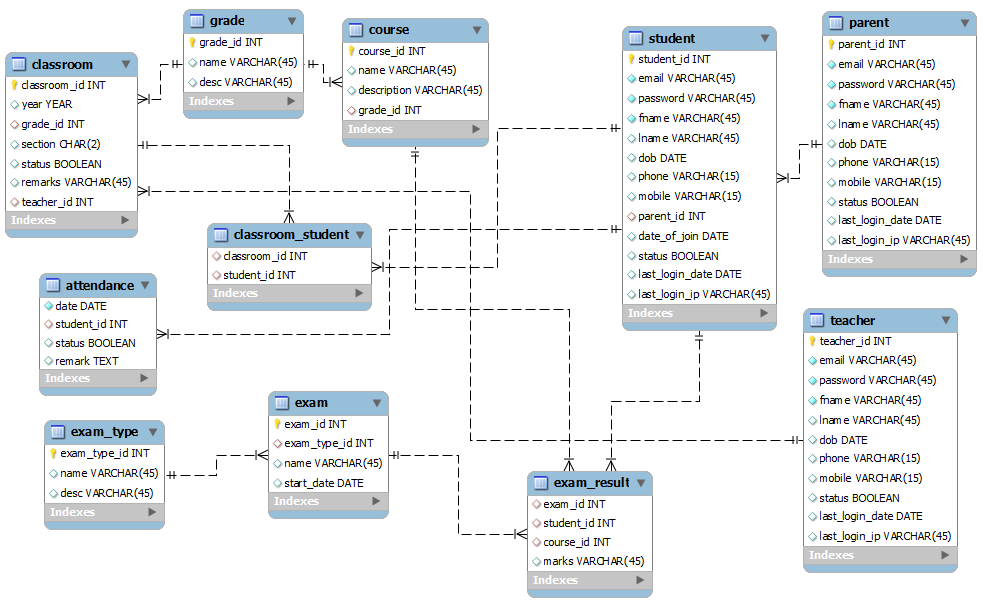
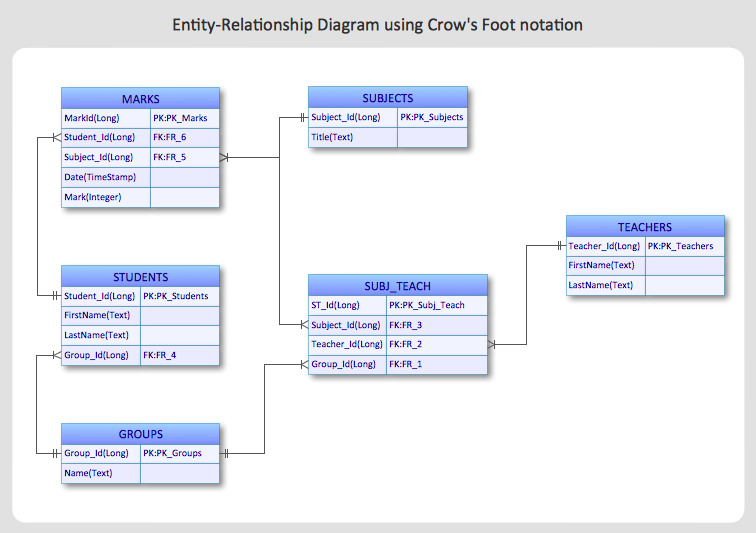
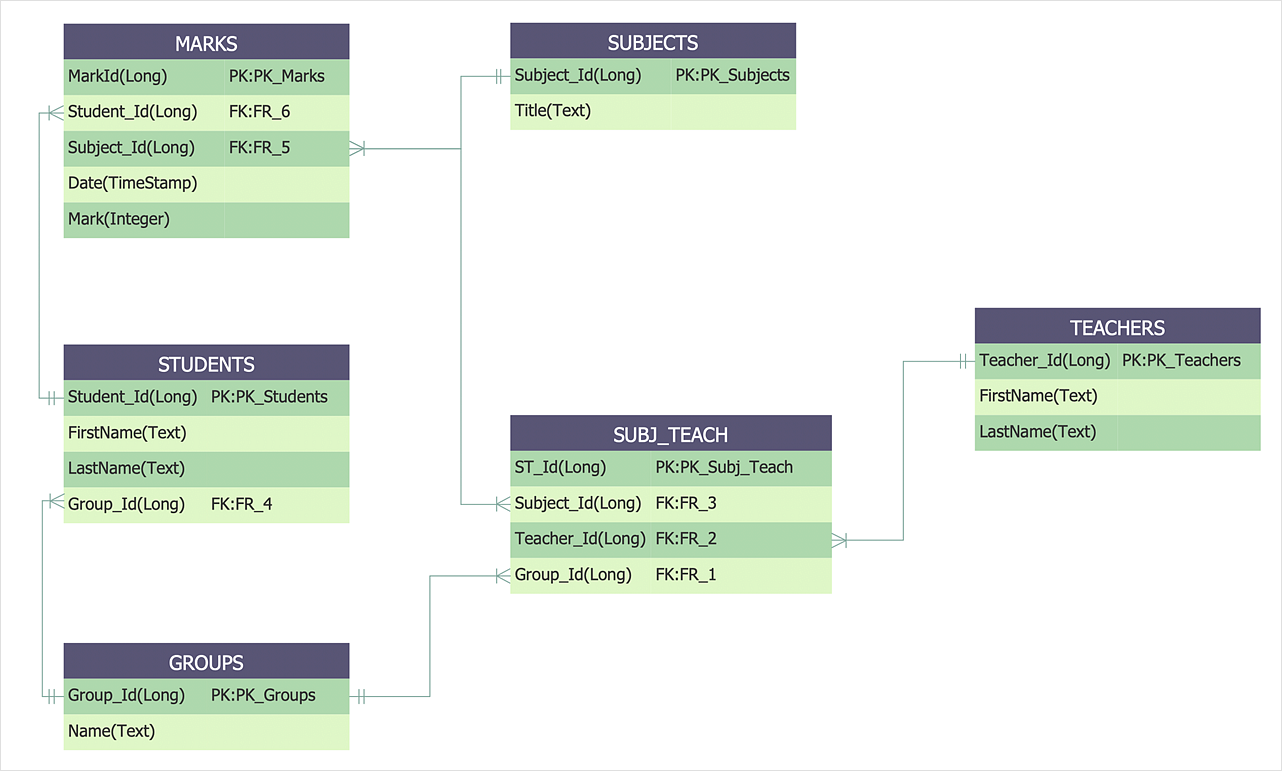
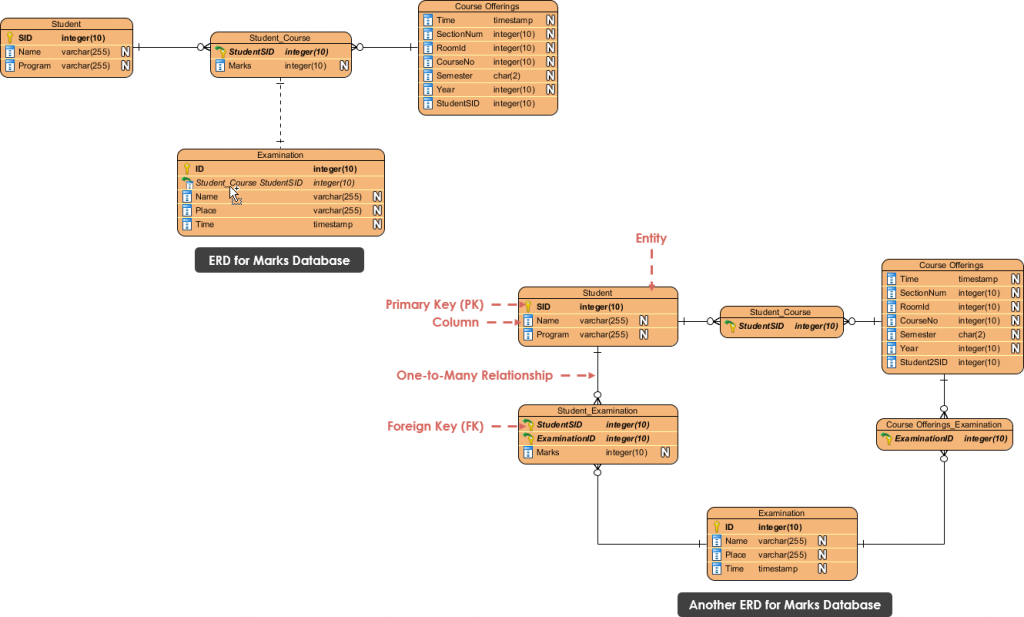
Relation Between Course And Teacher Database
Relation Between Course And Teacher Database - Learn how to draw an er diagram for a university database application using dbms concepts effectively. During course planning, the teaching instructor is an important person to indicate and decide the effective teaching approach and. The business rules are : For example, a single row in courses. Each table must include a primary key column. There was strong interest in prioritizing the creation of additional training materials for ggb database use and data submission, as well as specifically for formal educational. However, i get stuck in the second rule. Subject can have many sections and a section can have many. In this form, each entry in one table relates to many rows in a different table. 1) a professor can teach many courses. For example, a single row in courses. What would be the right relationship for this? The business rules are : For example, create relationships between “students” and “courses” to associate students with the courses they’re enrolled in. This article covers all 5 types of relationships in sql tables. I'm designing a database where i have a course table and and professor table. Main problem here is the relationship between section and subject. Relationships in sql are a way to establish connections between multiple tables. In this form, each entry in one table relates to many rows in a different table. During course planning, the teaching instructor is an important person to indicate and decide the effective teaching approach and. Each table must include a primary key column. For example, create relationships between “students” and “courses” to associate students with the courses they’re enrolled in. Select b.id as batch, t.name as teacher, s.name as student from takes k join teacher t on k.subject_id = t.subject_id join batch b on t.id = b.teacher_id join. In this form, each entry in one. This article covers all 5 types of relationships in sql tables. Select b.id as batch, t.name as teacher, s.name as student from takes k join teacher t on k.subject_id = t.subject_id join batch b on t.id = b.teacher_id join. For example, create relationships between “students” and “courses” to associate students with the courses they’re enrolled in. During course planning, the. It is also theoretically possible that 3 unique student records exist for the same student (i.e. The teacher manually created a record, then the system created it, then the student created an. What would be the right relationship for this? Select b.id as batch, t.name as teacher, s.name as student from takes k join teacher t on k.subject_id = t.subject_id. A primary key is a unique,. I'm designing a database where i have a course table and and professor table. It is also theoretically possible that 3 unique student records exist for the same student (i.e. This article covers all 5 types of relationships in sql tables. In the end, you're best off with at least three tables: The teacher manually created a record, then the system created it, then the student created an. There was strong interest in prioritizing the creation of additional training materials for ggb database use and data submission, as well as specifically for formal educational. The business rules are : However, i get stuck in the second rule. This article covers all 5. 1) a professor can teach many courses. It is also theoretically possible that 3 unique student records exist for the same student (i.e. The teacher manually created a record, then the system created it, then the student created an. I'm designing a database where i have a course table and and professor table. In the end, you're best off with. Select b.id as batch, t.name as teacher, s.name as student from takes k join teacher t on k.subject_id = t.subject_id join batch b on t.id = b.teacher_id join. I'm designing a database where i have a course table and and professor table. Subject can have many sections and a section can have many. In this form, each entry in one. I'm designing a database where i have a course table and and professor table. Each table must include a primary key column. However, i get stuck in the second rule. Main problem here is the relationship between section and subject. Relationships in sql are a way to establish connections between multiple tables. Relationships in sql are a way to establish connections between multiple tables. 1) a professor can teach many courses. For example, create relationships between “students” and “courses” to associate students with the courses they’re enrolled in. The teacher manually created a record, then the system created it, then the student created an. In this form, each entry in one table. It is also theoretically possible that 3 unique student records exist for the same student (i.e. In the end, you're best off with at least three tables: 2) on a given semester, a course can be offered on different. I'm designing a database where i have a course table and and professor table. 1) a professor can teach many courses. It is also theoretically possible that 3 unique student records exist for the same student (i.e. During course planning, the teaching instructor is an important person to indicate and decide the effective teaching approach and. 2) on a given semester, a course can be offered on different. This article covers all 5 types of relationships in sql tables. Subject can have many sections and a section can have many. 1) a professor can teach many courses. For example, create relationships between “students” and “courses” to associate students with the courses they’re enrolled in. The business rules are : For example, a single row in courses. What would be the right relationship for this? Learn how to draw an er diagram for a university database application using dbms concepts effectively. A primary key is a unique,. Relationships in sql are a way to establish connections between multiple tables. The teacher manually created a record, then the system created it, then the student created an. There was strong interest in prioritizing the creation of additional training materials for ggb database use and data submission, as well as specifically for formal educational. However, i get stuck in the second rule.Entity Relationship Diagram Class Student Teacher Data Model
Solved Consider a database that includes the entity
School Management System Project Database Design Techprofree
EntityRelationship Diagram (ERD) EntityRelationship Diagram (ERD
Relational Database Design
Relational Database Design
Creating ERD diagram ConceptDraw HelpDesk
Entity Relationship Diagram Example Student Score Visual Paradigm
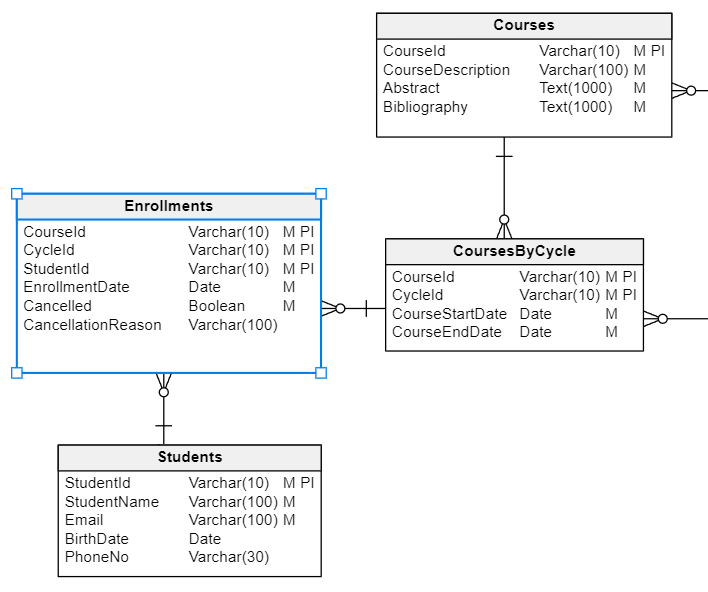
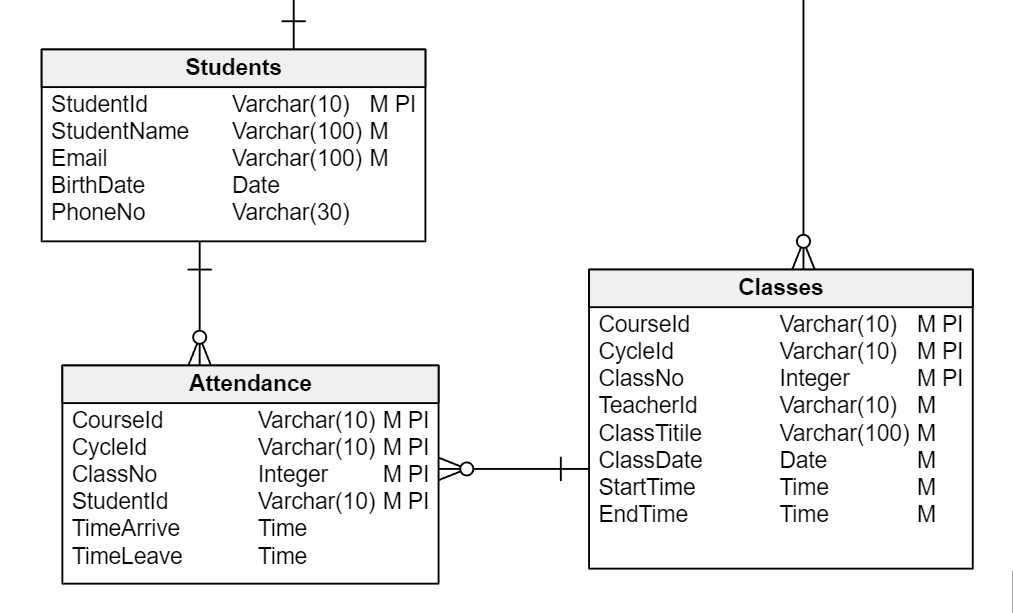
Database Design for a Learning Management System Vertabelo Database
Database Design for a Learning Management System Vertabelo Database
In The End, You're Best Off With At Least Three Tables:
I'm Designing A Database Where I Have A Course Table And And Professor Table.
In This Form, Each Entry In One Table Relates To Many Rows In A Different Table.
Select B.id As Batch, T.name As Teacher, S.name As Student From Takes K Join Teacher T On K.subject_Id = T.subject_Id Join Batch B On T.id = B.teacher_Id Join.
Related Post: