Course Of Saphenous Nerve
Course Of Saphenous Nerve - Learn its course and anatomy. The course of the main branches, number of collateral. Explore the anatomy and role of the saphenous nerve in the thigh and leg with innerbody's 3d model. The vagus nerve is a vital cranial nerve that controls parasympathetic functions in the body, from the brainstem to the abdomen! Anesthesia of the medial lower leg can be achieved by blocking either the femoral or saphenous nerves. Its origin from the femoral nerve, extensive course through the. The saphenous nerve, artery, and vein are integral structures of a neurovascular bundle that courses through the thigh and leg of the lower limb. Ten lower limb embalmed specimens were meticulously dissected, digitized, laser scanned, and modelled in 3d. The course of the saphenous nerve: The purpose of this study was to determine the distal limit of the saphenous nerve. The saphenous nerve is a major peripheral nerve of the thigh and medial leg. The saphenous nerve is a sensory nerve, which provides sensory innervation to the posteromedial aspect of the leg and the medial aspect of the foot. Its anatomy at the joint line of the knee. Ten lower limb embalmed specimens were meticulously dissected, digitized, laser scanned, and modelled in 3d. The infrapatellar branch of the. The saphenous nerve can be blocked anywhere along its course, from. The course of the main branches, number of collateral. However, the exact course and location of the distal saphenous nerve is not well described in the literature. Learn its course and anatomy. Shortly after the femoral nerve passes under the inguinal ligament, it splits into anterior and posterior divisions by the passage of the lateral femoral circumflex artery (a branch of the profunda femoris artery The saphenous nerve is the largest and terminal branch of the femoral nerve. The saphenous nerve is a sensory nerve that presents deep within the leg. This nerve plays a key role in providing sensation to the anteromedial, medial, and posteromedial regions of the. It is the longest sensory nerve in the human body and primarily. Its anatomy at the. The saphenous nerve is a clinically important nerve that may differ in its anatomical course among individuals and between the left and right limbs of a person. The saphenous nerve can be blocked anywhere along its course, from. The course of the main branches, number of collateral. The saphenous nerve is a sensory nerve, which provides sensory innervation to the. The saphenous nerve is the largest cutaneous branch of the femoral nerve. The infrapatellar branch of the. The saphenous nerve represents a critical sensory component of the lower extremity’s nervous system. Explore the anatomy and role of the saphenous nerve in the thigh and leg with innerbody's 3d model. The saphenous nerve is the largest and terminal branch of the. The course of the main branches, number of collateral. The saphenous nerve is a major peripheral nerve of the thigh and medial leg. Ten lower limb embalmed specimens were meticulously dissected, digitized, laser scanned, and modelled in 3d. The course of the saphenous nerve: It is the longest sensory nerve in the human body and primarily. The saphenous nerve is a sensory nerve that presents deep within the leg. The saphenous nerve is a clinically important nerve that may differ in its anatomical course among individuals and between the left and right limbs of a person. Firstly, the saphenous nerve is. Its anatomy at the joint line of the knee. Anesthesia of the medial lower leg. Explore the anatomy and role of the saphenous nerve in the thigh and leg with innerbody's 3d model. The saphenous nerve is a major peripheral nerve of the thigh and medial leg. The vagus nerve is a vital cranial nerve that controls parasympathetic functions in the body, from the brainstem to the abdomen! It is the longest sensory nerve in. The purpose of this study was to determine the distal limit of the saphenous nerve. It is purely a sensory nerve. It is the longest sensory nerve in the human body and primarily. Anesthesia of the medial lower leg can be achieved by blocking either the femoral or saphenous nerves. The course of the main branches, number of collateral. Ten lower limb embalmed specimens were meticulously dissected, digitized, laser scanned, and modelled in 3d. The saphenous nerve, artery, and vein are integral structures of a neurovascular bundle that courses through the thigh and leg of the lower limb. The saphenous nerve is a major peripheral nerve of the thigh and medial leg. The saphenous nerve is a sensory branch. Firstly, the saphenous nerve is. However, the exact course and location of the distal saphenous nerve is not well described in the literature. Explore the anatomy and role of the saphenous nerve in the thigh and leg with innerbody's 3d model. Learn its course and anatomy. It is purely a sensory nerve. Explore the anatomy and role of the saphenous nerve in the thigh and leg with innerbody's 3d model. Anesthesia of the medial lower leg can be achieved by blocking either the femoral or saphenous nerves. Firstly, the saphenous nerve is. The vagus nerve is a vital cranial nerve that controls parasympathetic functions in the body, from the brainstem to the. The saphenous nerve is a sensory branch of the femoral nerve, originating from the l3 and l4 spinal nerves. Explore the anatomy and role of the saphenous nerve in the thigh and leg with innerbody's 3d model. Anesthesia of the medial lower leg can be achieved by blocking either the femoral or saphenous nerves. Shortly after the femoral nerve passes under the inguinal ligament, it splits into anterior and posterior divisions by the passage of the lateral femoral circumflex artery (a branch of the profunda femoris artery The saphenous nerve is a clinically important nerve that may differ in its anatomical course among individuals and between the left and right limbs of a person. The course of the main branches, number of collateral. However, the exact course and location of the distal saphenous nerve is not well described in the literature. The saphenous nerve is a sensory nerve that presents deep within the leg. Ten lower limb embalmed specimens were meticulously dissected, digitized, laser scanned, and modelled in 3d. The saphenous nerve is a sensory nerve, which provides sensory innervation to the posteromedial aspect of the leg and the medial aspect of the foot. The course of the main branches, number of collateral. The saphenous nerve, artery, and vein are integral structures of a neurovascular bundle that courses through the thigh and leg of the lower limb. This nerve plays a key role in providing sensation to the anteromedial, medial, and posteromedial regions of the. The vagus nerve is a vital cranial nerve that controls parasympathetic functions in the body, from the brainstem to the abdomen! The saphenous nerve can be blocked anywhere along its course, from. Its origin from the femoral nerve, extensive course through the.Saphenous Nerve Anatomy, Pain, and Treatment Portland
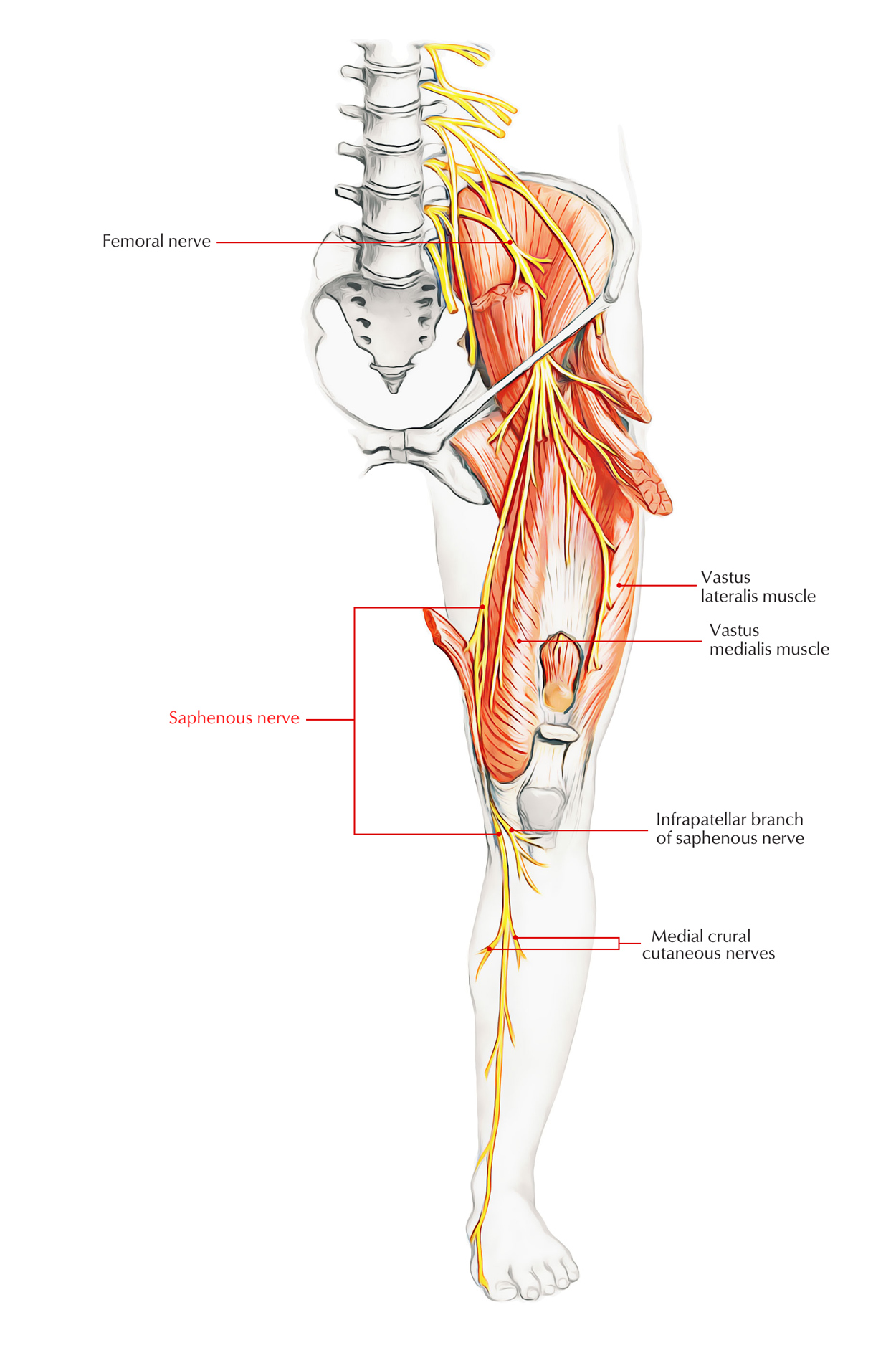
The Femoral Nerve Course Motor Sensory TeachMeAnatomy
Saphenous Nerve Course Abba Humananatomy
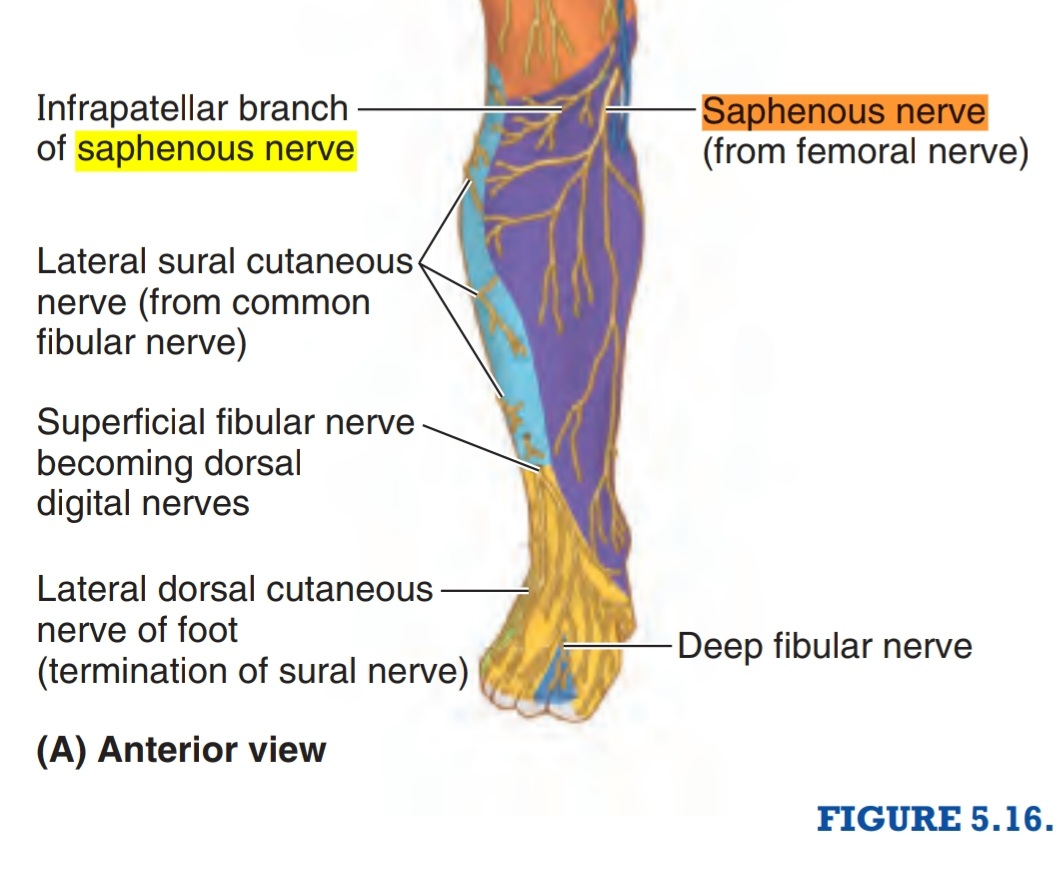
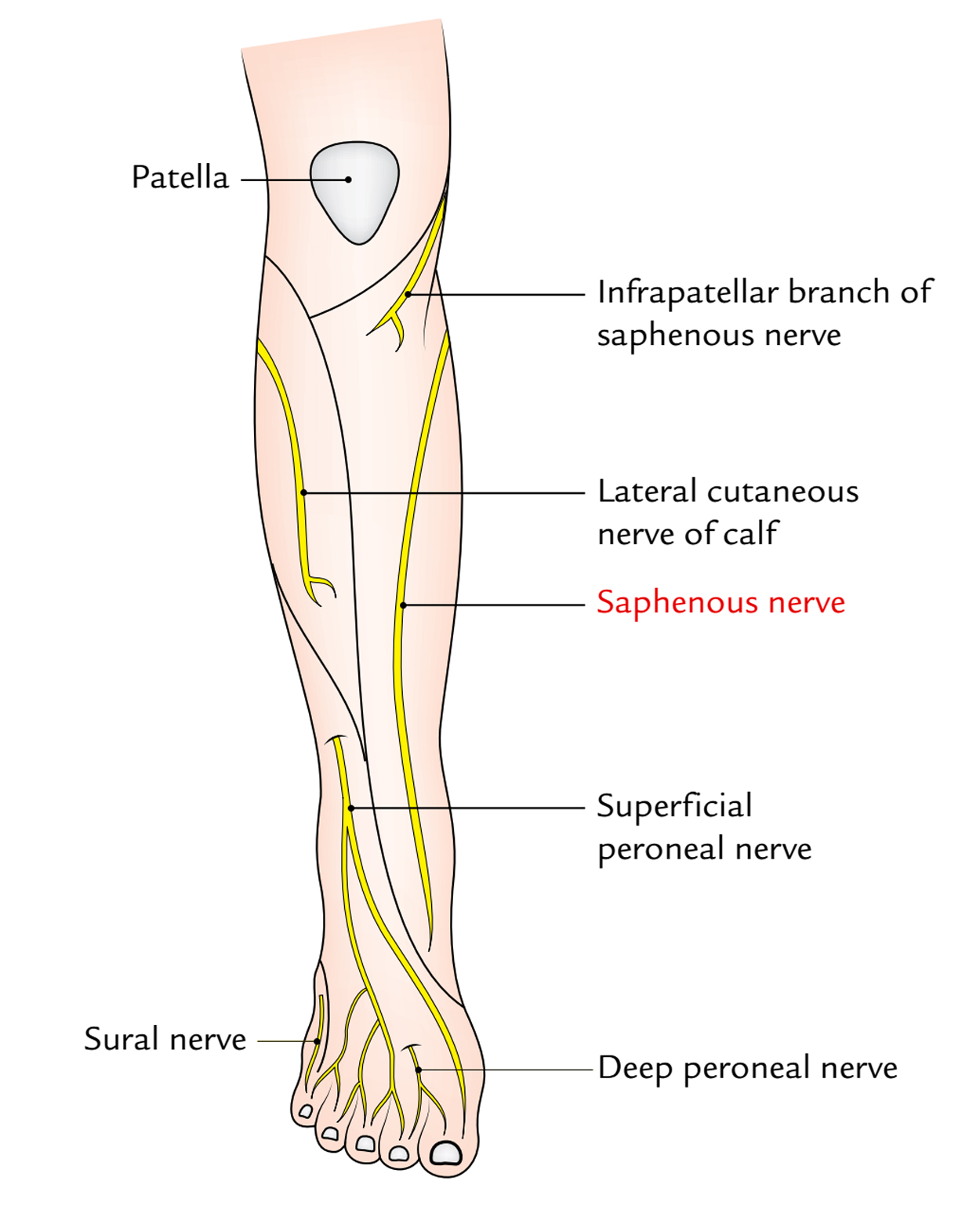
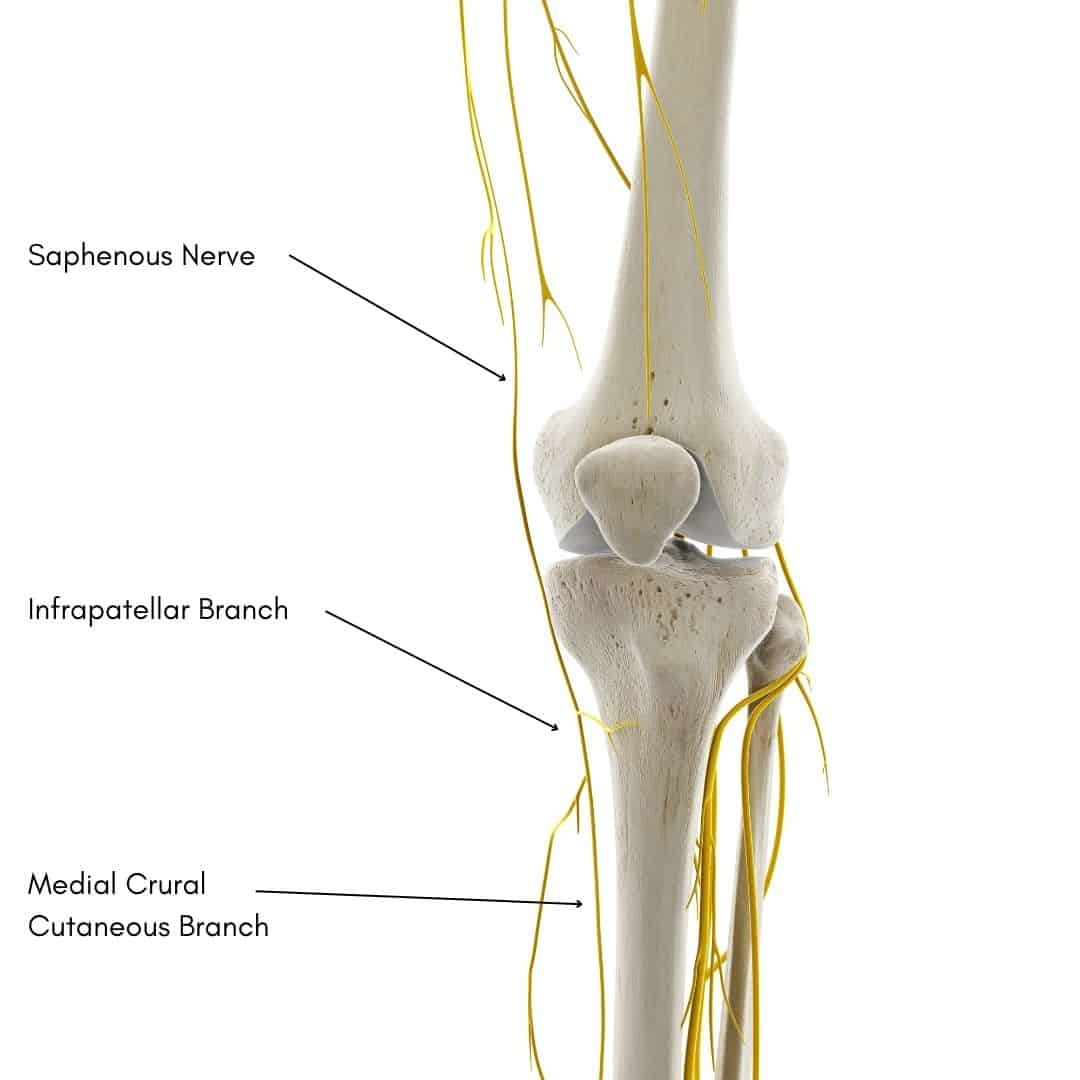
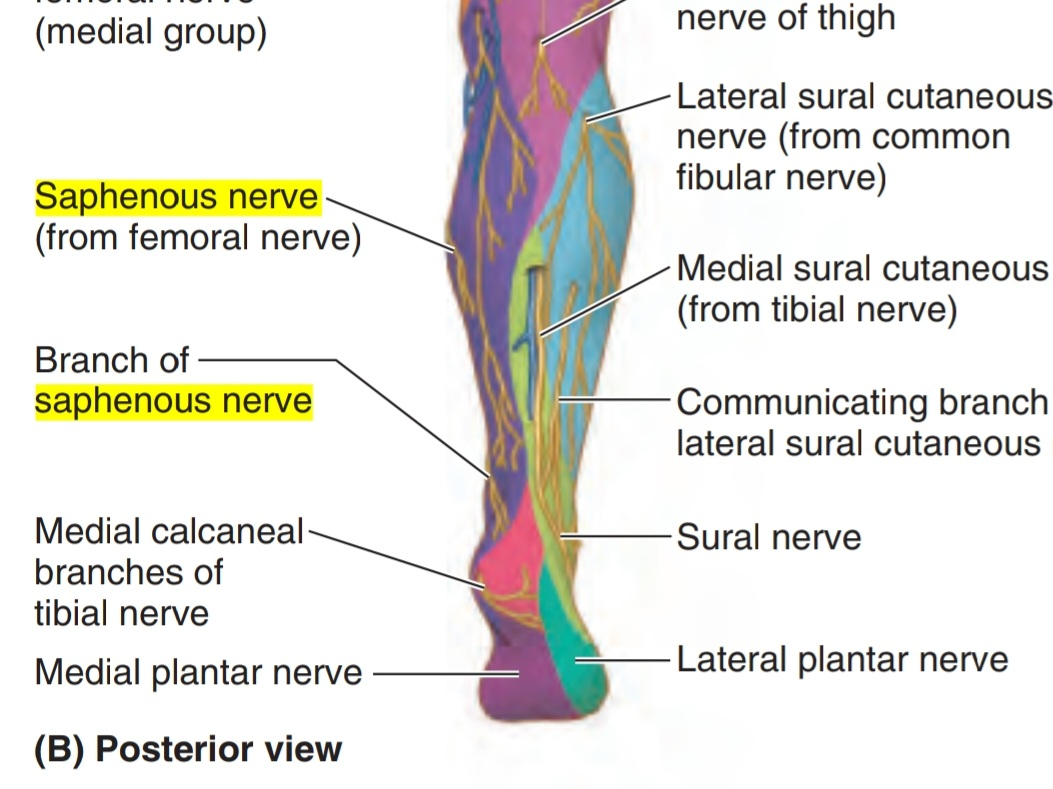
Saphenous nerve
Saphenous Nerve Course Abba Humananatomy
Panel A illustration of the saphenous nerve and the two different
Saphenous Nerve Anatomy and Function
4 Saphenous nerve anatomy (Image by Springer) Download Scientific Diagram
Saphenous Nerve Earth's Lab
Saphenous nerve
The Saphenous Nerve Is The Largest And Terminal Branch Of The Femoral Nerve.
Ten Lower Limb Embalmed Specimens Were Meticulously Dissected, Digitized, Laser Scanned, And Modelled In 3D.
The Saphenous Nerve Represents A Critical Sensory Component Of The Lower Extremity’s Nervous System.
Learn Its Course And Anatomy.
Related Post: